Onion vs. Garlic — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Garlic is denser in nutrients, providing more carbs and protein. Garlic contains ten times more vitamin B6 and four times more vitamin C, while onion has higher amounts of folate. Garlic is a better source of minerals, including iron, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, calcium, magnesium, and especially copper.
Introduction
Garlic and onion are different vegetables with important nutrient content. This article will discuss their differences regarding the nutritional profile and health impact.
Garlic is a bulbous flowering plant widely used as a flavoring and medicine in different dishes. It is a well-known flavoring in Chinese cuisine.
Onion is a famous blub vegetable cultivated worldwide, usually in regions with a moderate climate and well-drained soils. Onion is commonly used as a flavoring for sandwiches, salads, soups, and other dishes. It can be consumed alone, in grilled, roasted, deep-fried, or caramelized forms.
As the classification indicates, garlic and onion are two species from the same genus - Allium.
Actual differences
Although both are close relatives, garlic and onion, differ in taste, smell, and appearance.
An onion is a yellow, red, or white globe-shaped bulb. The bulb consists of multilayered leaves that store all the essential nutrients for the plant.
Garlic is a bulbous vegetable too, but the garlic bulb holds approximately 20 white cloves instead of leaves. Garlic is covered with thin, membrane-like skin, while onion has a thick peel.
Onions have a wide range of flavors: tangy or umami, sour or sweet, soft or crisp. Garlic has a unique taste: when it is raw, it can be described as a spicy flavor, but when it is cooked, it turns out to be nutty.
Crushed garlic smells pungent, while onion has a sulfurous odor with a metallic nuance.
Nutrition
In the infographics below, you can find information about the nutritional composition of 100g servings of onion and garlic.
The average serving size for these vegetables is one cup, chopped, equalling 160g for onion and 136g for garlic.
Macronutrients
Garlic is much denser in nutrients than onion. Onion contains 89% of water, 9% of carbs, and 2% of other nutrients, while garlic has 59% of water, 33% of carbohydrates, 6% of protein, and 2% of other nutrients.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+52.1%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+478.2%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+400%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+254%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+328.6%
Calories
Onion is classified as a low-calorie food, while garlic lies in the medium-calorie food list.
Garlic is significantly higher in calories, containing 109 more calories per every 100g. In each 100g, onion contains 40 calories, while garlic provides 149 calories.
Carbohydrates
Garlic is 23.4g higher in net carbs than onion in every 100g serving, while onion contains 1.3g of fructose that lacks in garlic, resulting in onion being sweeter than garlic.
100g serving size of onion contains 9.3g of carbs, 82% of which are net carbs and 16% - dietary fiber, while the exact size of garlic provides 33.1g of carbs, 94% of which are net carbs and 6% - dietary fiber.
Onion and garlic are good sources of dietary fiber. Both of them are especially rich in soluble fiber.
Protein
Garlic is six times higher in protein, containing 6.4g per 100g, while onion has 1.1g. It is known that most garlic proteins act as immune system-modulating agents. However, their identities and structures have not been described yet (1).
Fats
Garlic and onion contain less than one gram of fat per 100g. Hence, the fat content can be neglected.
Most of the fats present in onions are saturated. Garlic contains primarily polyunsaturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-52.8%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+18.2%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+1364.7%
Vitamins
Garlic is higher in most vitamins, containing ten times more vitamin B6, nearly four times more vitamin C, and overall more vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, E, A, and K.
Onion has more than six times more vitamin B9 /folate/ than garlic.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+533.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+321.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+300%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+334.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+307.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+503.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+384.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+929.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+325%
Minerals
Garlic is the winner in this section as well. It is significantly higher in most minerals: iron, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, magnesium, calcium, and copper. Garlic covers 100% of the DV for copper.
Onion contains less sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-76.5%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+150%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+687%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+174.7%
Contains
more
IronIron
+709.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+666.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+582.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+427.6%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+1196.1%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+2740%
Glycemic index
Onion has an average GI of 15, fitting into the list of low-glycemic index foods. For more information, you can read this in-depth article: onion nutrition.
Garlic's average glycemic index equals 30, considering it a low-glycemic index food. However, garlic has a higher glycemic index than onion.
You can also look at our glycemic index chart page for more information about other foods' glycemic indexes.
Health impact
Cardiovascular health
Garlic and onion contain different compounds that help maintain cardiovascular health.
Onions produce a wide range of antioxidants - compounds that help fight oxidative stress and prevent damage to the organism. Quercetin is one of the antioxidants abundant in onions. It may benefit in lowering high blood pressure (2). Research shows that using onion extracts can notably decrease systolic blood pressure due to their quercetin content (3). Another study indicates that high amounts of red onions may lower LDL cholesterol concentrations (4).
Garlic reduces total blood cholesterol levels. It lowers LDL and total cholesterol concentrations by 10-15% (5) (6). However, garlic has a significant effect on LDL (bad) cholesterol levels rather than HDL cholesterol levels (7) (8).
Antioxidants
Onion and garlic are excellent sources of antioxidants. Onion contains different types of flavonoids - plant antioxidants that may benefit the human organism.
Anthocyanins are one of those flavonoids. They are abundant in red onions because they are plant pigments that give onion its color. Anthocyanins can inhibit cell proliferation in cancer pathogenesis and prevent diabetes (9) (10).
Garlic consumption leads to a higher concentration of antioxidant enzymes in the human organism. It contains antioxidants having anti-inflammatory effects (11). Garlic can reduce the risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease (12).
Bone Health
Garlic and onion benefit from increasing bone density and supporting bone health. However, this impact is due to the different mechanisms and chemicals these vegetables provide.
Garlic increases estrogen levels in postmenopausal women's blood. This leads to a lower risk of fractures and higher bone density (13) (14).
Some studies show that high onion consumption results in a lower risk of hip fracture and higher bone density (15) (16).
Digestive Health
Garlic and onion are not the best choices for people with IBS, as they are high in FODMAPs and may trigger the symptoms. They may cause bloating, gases, and abdominal pain in people without IBS too.
Garlic and onion may also trigger heartburn in some individuals (17) (18).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20004743/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7254783/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26328470/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24612081/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8169881/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10975959/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19060427/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17328819/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27646173/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29210634/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11238807/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16484570/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15173999/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21143861/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26686359/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19240657/
- Medicinal Use of Garlic
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2327378/
Infographic
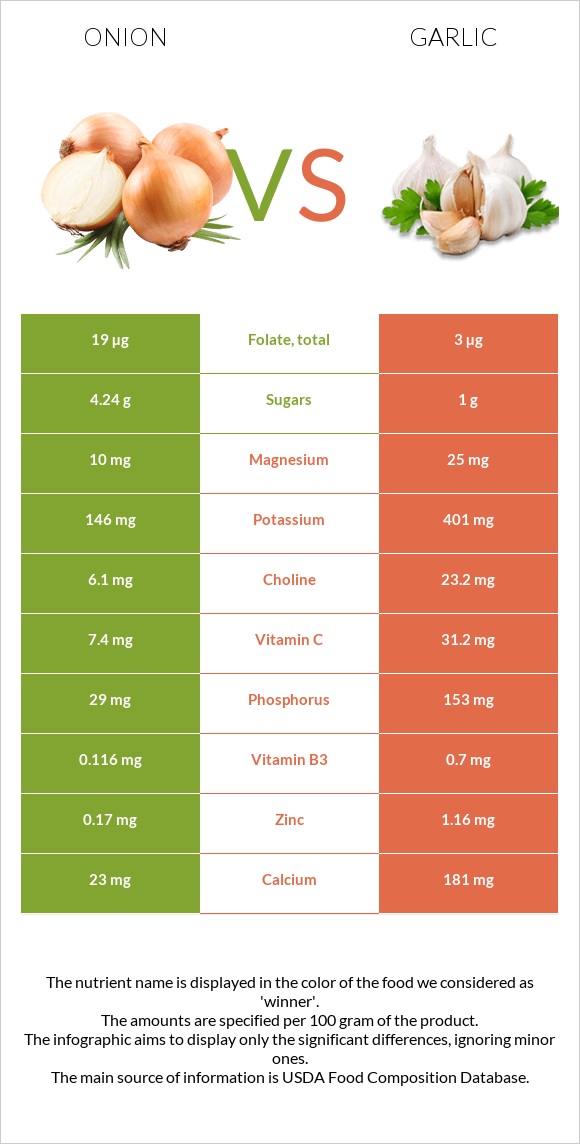
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.12mg | 1.235mg | 86% |
| Manganese | 0.129mg | 1.672mg | 67% |
| Copper | 0.039mg | 0.299mg | 29% |
| Vitamin C | 7.4mg | 31.2mg | 26% |
| Selenium | 0.5µg | 14.2µg | 25% |
| Iron | 0.21mg | 1.7mg | 19% |
| Phosphorus | 29mg | 153mg | 18% |
| Calcium | 23mg | 181mg | 16% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.046mg | 0.2mg | 13% |
| Protein | 1.1g | 6.36g | 11% |
| Zinc | 0.17mg | 1.16mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.123mg | 0.596mg | 9% |
| Carbs | 9.34g | 33.06g | 8% |
| Potassium | 146mg | 401mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.027mg | 0.11mg | 6% |
| Calories | 40kcal | 149kcal | 5% |
| Magnesium | 10mg | 25mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.116mg | 0.7mg | 4% |
| Folate | 19µg | 3µg | 4% |
| Choline | 6.1mg | 23.2mg | 3% |
| Fiber | 1.7g | 2.1g | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.017g | 0.249g | 2% |
| Fructose | 1.29g | 2% | |
| Fats | 0.1g | 0.5g | 1% |
| Sodium | 4mg | 17mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.4µg | 1.7µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 7.64g | 30.96g | N/A |
| Sugar | 4.24g | 1g | N/A |
| Vitamin E | 0.02mg | 0.08mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.042g | 0.089g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.013g | 0.011g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.014mg | 0.066mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.021mg | 0.157mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.014mg | 0.217mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.025mg | 0.308mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.039mg | 0.273mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.002mg | 0.076mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.025mg | 0.183mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.021mg | 0.291mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.014mg | 0.113mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Onion - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170000/nutrients
- Garlic - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169230/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





